Share this
Google Images SEO Best Practices
by Jin on Jul 19, 2022 8:30:00 AM
Contents
- UX Improvements
- Checking Page Titles and Descriptions
- Adding Structured Data
- Speed Optimization
- Using High Definition Images
- Adding Specific Titles, Captions, File Names, and Text to the Image
- Using Specific Alternative Text
- Helping Google Search for Images
- Responsive Image
- Optimizing for Safe Search

Google images allow you to visually find information on the web. New features such as image captioning and badges allow users to quickly explore more details and relevant information about the image. Adding image content increases the probability of attracting attention in search results, which can lead to high quality website traffic. Also, optimizing images and sites to Google images makes them easier to be exposed to by multiple users. So by using various strategies, try to increase the likelihood of content being exposed to Google image search results.
1. UX Improvements
To increase the searchability of content in Google images, you need to provide a satisfactory User Experience. The ultimate goal of Image SEO is to create pages for users, not for search engines.
1) Providing Appropriate Content
Verify that visual content is relevant to the page topic. If you are to add value by adding an image to the page, it is strongly recommended. However, we do not recommend using pages where images and text are not the original content.
2) Batch Optimization
Try to place the image near the relevant text, if possible. It is recommended that you place the most important image at the top of the page.
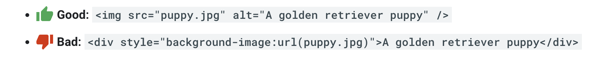
3) Not to Enter Important Text within the Image
Not everyone has access to the text, and the page translation tool does not recognize the image files. Therefore, important text elements such as page titles and menu items should not be included in the image. It is also recommended that you keep the text in HTML and provide an alternative text(Alt Text) for the image to ensure maximum accessibility.
4) Creating a Beneficial, High-Quality Site
The quality of web page content is as important as visual content for Google images. High-quality content provides information and makes results more practical. You can use the page content to create text snippets for images, and Google ranks images by the quality of page content.
5) Developing a Device-Friendly Site
The proportion of users searching for Google images on mobile devices has increased compared to desktops. Therefore, it is important to design the site for all device types and sizes. You can use the Mobile Affinity Test to test whether the page is functioning properly on your mobile device, and get feedback on what needs to be improved.
6) Creating an Appropriate URL Structure for the Image
Google uses URL paths and filenames to identify images. Organizing image content so that URLs are logically configured can help you identify the image efficiently.
2. Checking Page Titles and Descriptions
Google Images automatically generates titles and snippets that describe each search result most effectively. It also shows the association between search words and search results, helping users decide whether to click on the search results. Furthermore, Google generates additional information using a variety of sources, such as the title of each page and the descriptive information contained in the meta tag. As a result, you can improve the quality of titles and snippets that describe the page by referring to the title and snippet guidelines that Google provides.
3. Adding Structured Data
By including structured data, you can provide users with information about the page and display it as a result, including badges that can efficiently forward traffic to the site. This provides more useful information to users and enables users to be directed to sites with more effective and targeted traffic. Google Images support structured data for the following types:
Refer to the general structured data guidelines as well as the structured data type guidelines provided by Google. Image properties are required for each structured data type to display badge and rich results in Google Images.
4. Speed Optimization
Images are the biggest factor in determining the overall page size, which can slow down the page and increase the cost of loading. High quality, fast user experience with the latest image optimization and responsive image technology must be provided. Analyze the site speed with PageSpeed Insights and find recommendations and technologies to improve performance with Web basics.
5. Using High Definition Images
A clear image is more attractive to the user than a blurry image. In addition, if you use a clear image as a thumbnail from search results, you will be able to drive traffic by increasing the user’s click rate.
6. Adding Specific Titles, Captions, File Names and Text to the Image
Google extracts information about image topics, including captions and image titles, from the contents of the page. Therefore, it is recommended that you place the page associated with the image topic or the text associated with the image.
Furthermore, file names also help Google understand the image theme, so if you localize the image, you must convert the file names appropriately. For example, my-new-black-kitten.jpg is more effective than IMG00023.JPG in informing image topics.
7. Employing Specific Alternative Texts
Alternative text(Alt Text) which is used to describe an image improves accessibility for users who cannot see images on a web page, such as those using a screen reader or those with low bandwidth internet connections. Google utilizes computer vision algorithms, page content, along with alternative text to identify the subject of the image. Alternative text in an image can also be utilized as anchor text when an image is used as a link.
When typing alternative text, you should use keywords appropriately and focus on creating content that can deliver various information while matching the content of the page. Refrain from filling Alt attributes with keywords (keyword stuffing) because it negatively affects the user experience and can be considered a spam site. If necessary, add alternative properties according to the W3 guidelines, taking into account the accessibility of alternative text.

8. Helping Google Search for Images
Using Semantic Markup for Images
Google analyzes HTML on pages to index images, but not on CSS images.
Using Image Sitemap
Image sitemaps allow Google to provide URLs for images that may not otherwise be found. Image sitemaps can contain URLs from other domains, unlike regular sitemaps that restrict cross domains. This allows you to host images using a content delivery network (CDN).
Supported Image Types
Google Images support images in BMP, GIF, JPEG, PNG, WebP, and SVG formats. Images can also be inlined in the form of data URIs. The data URI can include image files inline by setting the src of the img element to the Base64 encoding string using the following format.
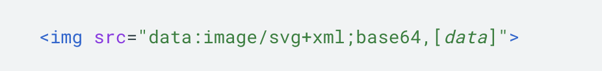 Inserting an inline image can reduce HTTP requests, but it should be careful because the size of the page can increase significantly.
Inserting an inline image can reduce HTTP requests, but it should be careful because the size of the page can increase significantly.
9. Responsive Image
Designing responsive web pages for users to use on a variety of devices can provide better user experience. Web pages specify responsive images using the <img srcset> property or <picture> element, but it is always recommended that you designate an alternate URL using the img src property because some browsers and crawlers do not recognize these properties.
If you use the srcset property, you can specify different versions of the same image depending on the screen size.

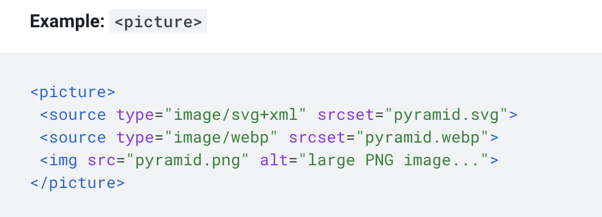
The <picture> element is a container used to group different <source> versions of the same image. It provides a preliminary approach for the browser to select the correct image based on device features such as pixel density and screen size. The <picture> element is also useful for using a new image format with graceful degradation, which is built in for clients that may not yet support the new format. When using the picture tag as shown below, it is always better to provide the imp element as a fallback with the src attribute.
10. Optimizing for Safe Search
SafeSearch is a Google Search and Google Image feature that prevents inappropriate or obscene content from being included in search results. Searchers can set whether to use it or not on their own. Therefore, SafeSearch finds most of the links excluding obscene videos, images, and pornography.
Receive Free Consultation of SEO AUDIT